elisa test od|elisa blood test : purchasing ELISA is a biochemical assay used in immunology to detect the presence of an antigen, antibody, or another protein. It takes its name from the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).. The basic principle behind ELISA is that if an antigen or antibody is present in a sample, it will bind to a specific antibody or antigen attached to a solid support. Find an autoclave or sterilizer that will sterilize all instruments. Distributors of Sterilizers & Autoclaves. On site sterilizer repairs!
{plog:ftitle_list}
Pressure plays a complementary role in autoclave sterilization, enhancing the penetration of steam into the materials and facilitating more thorough microbial destruction.
ELISA is a common laboratory testing technique that detects and counts certain antibodies, .The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological assay commonly used .
ELISA Data Interpretation. The ELISA assay yields three different types of data output: Quantitative: ELISA data can be interpreted in comparison to a standard curve (a serial dilution of a known, purified antigen) in order to precisely calculate the concentrations of antigen in various samples.ELISA is a biochemical assay used in immunology to detect the presence of an antigen, antibody, or another protein. It takes its name from the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).. The basic principle behind ELISA is that if an antigen or antibody is present in a sample, it will bind to a specific antibody or antigen attached to a solid support. ELISA test results, what does a positive ELISA test tell you? ELISA results may be interpreted quantitatively, qualitatively or semi-quantitatively . In a quantitative assay, a serial dilution of a known standard is used to enable the generation of a standard curve, normally of optical density (OD) versus concentration. How Is the ELISA Test Performed? A blood sample is needed. Most of the time, blood is drawn from a vein located on the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. The sample is sent to a laboratory where the targeted antibody or antigen is linked to a specific enzyme. If the target substance is in the sample, the test solution turns a .
What is an ELISA? The basic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), or enzyme immunoassay (EIA), is distinguished from other antibody-based assays because separation of specific and non-specific interactions occurs via serial binding to a solid surface, usually a polystyrene multiwell plate, and because quantitative results can be achieved.ELISA is an abbreviation for "enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay." In 1974, P. Perlmann and E. Engvall developed the test as a substitute for certain radioimmunoassay tests, and eventually, it replaced the western blot test for HIV confirmation. The ELISA test is versatile and medical professionals can perform it easily as compared to other more complicated tests; many . ELISA, short for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, is a widely used laboratory technique that detects and measures the presence of specific antibodies or antigens in a sample. It involves the binding of target molecules (antibodies or antigens) to a solid surface, followed by the addition of enzymes or fluorescent markers to generate a detectable signal. ELISA is .
ELISA tests are categorized into three categories based on the methods applied to bind antigen and antibodies, namely: Indirect and Direct ELISA. The crucial step is to immobilize the antigen of interest, which can be done directly on the test plate or indirectly via a . enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), biochemical procedure in which a signal produced by an enzymatic reaction is used to detect and quantify the amount of a specific substance in a solution. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) typically are used to detect antigens, though they can also be used to detect other substances, including .ELISA is a plate-based assay that uses antibodies to specifically detect and quantify the amount of a target antigen in a liquid sample. . (OD) in peripheral wells compared to central wells). . signal, compared to the standard control that is only in standard diluent. These issues are known matrix effects. To test if matrix effects are .The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological assay commonly used to measure antibodies, antigens, proteins and glycoproteins in biological samples. Some examples include: diagnosis of HIV infection, pregnancy tests, and measurement of cytokines or soluble receptors in cell supernatant or serum. . (OD). Figure 2. A typical .
An enzyme immunoassay (EIA) or an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a blood or urine analysis that can help diagnose many infections and inflammatory conditions. This is a simple test that does not cause side effects. Your EIA can help in diagnosing the cause of your symptoms and is used to guide your therapy.When developing any new ELISA, it is important to test several different blockers for the highest signal to noise ratio in the assay. Many factors can influence nonspecific binding, including various protein-protein interactions unique to the samples and antibodies involved. The most important parameter when selecting a blocker is the signal to .
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological technique extensively used in research and clinical laboratory settings to quantitatively identify a specific protein (i.e., the antigen or biomarker) in a biological matrix while relying on the principle of the specific binding interaction between the antigen and the antibody against the antigen of interest . Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) use the catalytic properties of enzymes to detect and quantify immunologic reactions. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a heterogeneous EIA technique used in clinical analyses. In this type of assay, one of the reaction components is nonspecifically adsorbed or .Over the past three decades, ELISA or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, has become vital to many areas of research and has shown to have many applications—from detecting food and environmental contaminants to screening for HIV and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) antibodies ELISA overview. ELISA is a method used to quantitatively detect an antigen (i.e., toxin or foreign .An example of a competition ELISA to test for antigen based on the direct detection method is shown in Figure 5 . Remove liquid and wash plate Remove liquid and wash plate Remove liquid and wash plate Remove liquid and wash plate In this example the antigen concentration in the sample was low. The
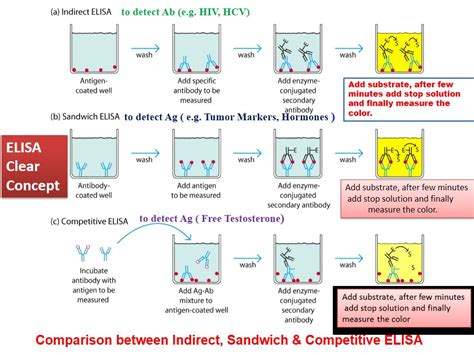
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay) is an immunologic technique used to detect the presence and concentration of an antigen or antibody in a sample. The power of an ELISA is based on the extreme specificity of the antigen-antibody interaction. ELISAs have wide-ranging applications, especially as medical diagnostic tools. Figure 1. ELISA . Diagram of a sandwich ELISA test. The difference between indirect ELISA and direct ELISA. The only difference in indirect and direct ELISAs (Figure 2) is the detection antibody used. In a direct ELISA, only one antibody is used. This single, primary antibody is conjugated directly to the detection enzyme. The indirect ELISA begins the same way .ELISA is used to detect the presence and to quantify specific antigens or antibodies. ELISA being an immunoassay method is very sensitive and specific in nature whereby the specific antigens or antibodies bind to their homologous antibodies and antigens, respectively. Overview of ELISA Test. ELISA is performed on a Microtitre plate. A .
laboratory autoclave manufacturers in mumbai
Sample containing primary antibody (Ab 1) or serum is added to the microtiter well coated with antigen and allowed to react with attached antigen to the well.[Fig – A & B] Free Antibody (Ab 1) is washed, bound antibody-antigen is detected by adding an enzyme-conjugated secondary antibody, which binds the primary antibody (Ab 1). [Fig C] Free secondary antibody, .
od definition in elisa
Why is an ELISA test so sensitive? ELISAs tend to be the most sensitive immunoassays due to the binding characteristics of the antibodies and the amplification or different read-out systems used. Sample volumes can also be adjusted when you have a very low abundant protein. As discussed above, indirect ELISAs allow for the amplification of .
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a qualitative or quantitative test that uses antibodies to bind and measure a molecule of interest. Similar to other immunoassays, both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies can be utilized to identify the analyte (eg, peptides, proteins, antibodies, small molecules).Variations between ELISA protocols A. Antigen Immobilization Antigen immobilization varies between two principle techniques. In a traditional (direct coating) ELISA, antigens are directly attached to the plate by passive adsorption, usually using a carbonate/bicarbonate buffer at pH >9. Most but not all proteins Test ELISA accuracy by diluting a spiked sample (1:2, 1:4, 1:8). This step helps to visualize the linearity and accuracy of the assay. 2. Compare the OD values of the diluted samples against the standard curve. Charts can be useful for this comparison. 3. The results should show a linear relationship; that is, the OD should decrease .
laboratory autoclave manufacturers india
ELISA stands for enzyme-linked immunoassay. It is a commonly used laboratory test to detect antibodies in the blood. An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmfulThe method for antigen capture will depend on the ELISA type selected: Direct ELISA - Enzyme conjugated antibody binds to antigen on a surface. Indirect ELISA - Similar to direct ELISA, but primary binding antibody is not conjugated. A second conjugated antibody is used to detect the primary antibody.
elisa test wikipedia
Esso ha lo scopo di alzare o abbassare il punto d’intervento al decrescere della pressione, ossia ad anticipare o ritardare la chiusura del contatto elettrico e quindi .
elisa test od|elisa blood test